What you need to know about Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be)
In early 2024, the Wi-Fi Alliance officially certified the new Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) wireless standard and published its specifications.
Wi-Fi 7 combines the advantages of the previous Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) standard and offers some new innovative solutions aimed at increasing Wi-Fi performance and improving connections in various conditions.
Important
Wi-Fi 7 is backwards compatible with previous generations (Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6), so your older devices will continue to connect to Wi-Fi 7 networks without any problems.
To take full advantage of Wi-Fi 7, you will need new devices that support Wi-Fi 7 on your router and client devices (smartphone, tablet, laptop, etc.).
Wi-Fi 7 supports simultaneous operation in three bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz*.
* — Due to regulatory restrictions, the 6 GHz band may not be available in some countries.
Compared to previous generations of standards, IEEE 802.11be has a number of unique innovations, the main ones being:
Technology - Multi-Link Operation;
MU-MIMO 16x16;
320 MHz channel width;
4096-QAM modulation;
Preamble Puncturing technology;
Reduced latency and interference resistance.
Multi-Link Operation technology
The main feature of the Wi-Fi 7 standard is the implementation of Multi-Link Operation (MLO) technology, which allows your device to connect to multiple bands simultaneously. In previous standards, the connection between two devices occurred in only one band, and the client itself determined whether to connect in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band, depending on network congestion, signal quality, and other parameters. The new standard allows you to use all three frequency bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz, simultaneously. A Wi-Fi 7 router will not transfer a client between bands, but will allow all available frequencies to be used at once. This will make the connection more stable and faster, ensure seamless connectivity when moving around the home or office, increase bandwidth, reduce latency, and improve the reliability of wireless connections.
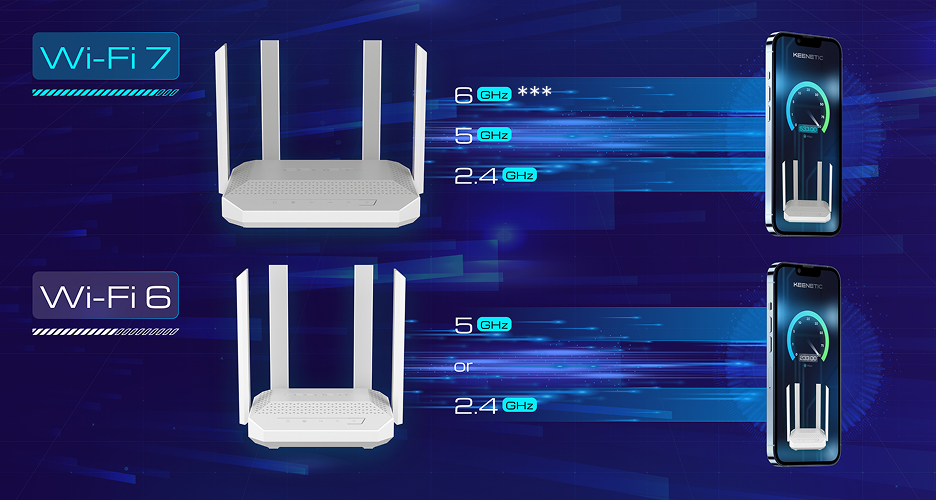

*** Wi-Fi 7 enables tri-band connectivity as part of its capabilities. The Ultra (NC-1812) is a dual-band device and does not support tri-band operation.
MU-MIMO 16x16
In the Wi-Fi 7 standard, the maximum number of MU-MIMO spatial streams has doubled from 8 to 16. This technology allows for more efficient use of available bandwidth without reducing overall network performance, while serving more client devices simultaneously. This means that every client in a home or office network, whether watching movies, playing games, or making video calls, can enjoy a faster and more reliable connection without slowing down other clients.
To take advantage of MU-MIMO 16x16, the Wi-Fi access point and wireless client must have 16 transmitters, 16 receivers, and 16 spatial streams (written as 16x16:16 or 16Tx16R:16SS). Currently, there are no clients that support this configuration. Most modern wireless devices support MIMO 1x1, 2x2, or 4x4 configurations.
320 MHz channel width
The Wi-Fi 7 standard supports ultrawide 320 MHz channels, which are twice as wide as those in Wi-Fi 6, which used channels up to 160 MHz wide. This significantly increases data throughput and is achieved by combining several adjacent channels into one wide channel.
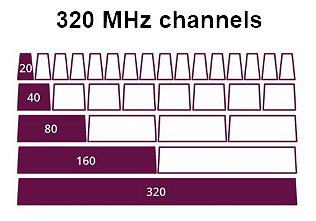
Support for 320 MHz channel width is only possible with the 6 GHz band and ideal radio conditions. Please note that due to regulatory restrictions, the 6 GHz band is not available for use in consumer Wi-Fi in some countries.
4096-QAM modulation
Wi-Fi 7 implements support for 4096-QAM quadrature amplitude modulation, also known as 4K-QAM. In 4096-QAM, the length of each coding symbol is increased from 10 bits (in 1024-QAM in the Wi-Fi 6 standard) to 12 bits. This increases the data transfer rate and spectrum efficiency by approximately 20%, as more data will fit into each packet.
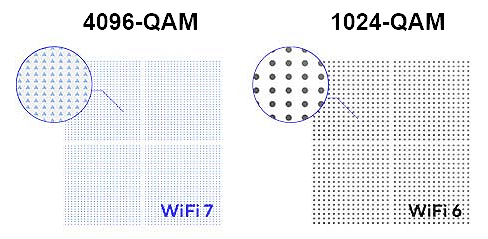
This improvement only works in conditions where the signal level is high and the noise is low. To achieve such high modulation, free radio air is required. If there is noise and interference in the ether, this modulation may not work.
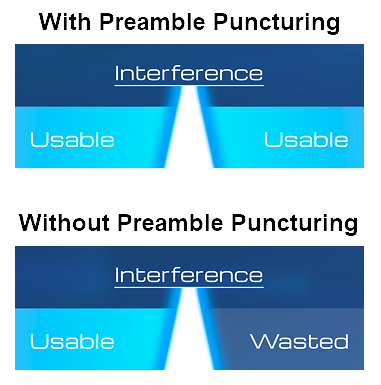
Preamble Puncturing Technology
Preamble Puncturing allows the router to 'skip' damaged sections of the channel when interference occurs, when possible. Previously, the entire channel would have been unavailable to other devices, but Preamble Puncturing technology allows only the problematic section to be bypassed, leaving the rest of the channel open for data transmission. By using available frequencies as efficiently as possible, this provides higher speeds and a stable, reliable connection, even in busy network environments.
Tip
Support for Multi-Link Operation, MU-MIMO 16x16, Preamble Puncturing technologies, as well as an increase in channel width to 320 MHz and improved modulation to 4096-QAM, provides a theoretical maximum data transfer rate of 46 Gbps on the Wi-Fi 7 standard, which is approximately 5 times higher than the maximum possible speed on the Wi-Fi 6 standard, which was 9.6 Gbps.
Wi-Fi 7 is also known as Extremely High Throughput (EHT).
The specified maximum data transfer rate can only be achieved under ideal radio conditions and with support for the above Wi-Fi 7 technologies on the wireless client and access point side. The actual real-world throughput of a Wi-Fi network will depend on a number of conditions, such as client limitations, client distance from the Wi-Fi access point, obstacles between Wi-Fi devices, radio interference, room layout, client location, and other environmental factors.
Reduced latency and interference resistance
Minimal delays are important for gaming, 3D technologies, real-time protocol (RTP) applications, virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR), Internet of Things (IoT) devices, online conferencing, video calls, and other applications that are highly sensitive to latency and jitter and are increasingly used in wireless connections. The Wi-Fi 7 standard significantly reduces latency compared to Wi-Fi 6, making it the optimal solution for such tasks.
Wi-Fi 7 adds support for TSN (Time-Sensitive Networking) technology, which allows latency-sensitive traffic to be prioritized and ensures reliable delivery of time-synchronized packets. Wi-Fi 7 devices dynamically allocate the necessary bandwidth to such traffic, ensuring the best possible response.
In all previous standards, interference on the channel led to a significant drop in data transfer speed. Wi-Fi 7 uses FCU (Flexible Channel Utilization) technology. When interference appears on the channel, the network will only use the 'clean' part of it, which will reduce the number of unrecognized 'broken' packets and increase the data transfer speed in interference conditions.
In addition to the technologies mentioned above, Wi-Fi 7 improves security with mandatory WPA3 support and enhanced encryption protocols for better protection against cyber threats, while maintaining the convenience and simplicity of connecting devices.
Who will benefit most from Wi-Fi 7?
For the average user, the capabilities of Wi-Fi 7 may seem excessive, but the new standard will be important for fast downloads of large amounts of information, stable operation of 3D technologies, VR/AR virtual reality applications, video conferencing, gaming, and working with cloud technologies.
The increased bandwidth of Wi-Fi 7 supports more users and larger data streams. MLO technology ensures that important video calls are clear, smooth, crisp, and uninterrupted, while 4K-QAM modulation speeds up file transfers. Reliable, high-performance Wi-Fi 7 connections will be in demand for both busy office workers and customers in bustling cafes.
Gamers demand instant response. The fast speeds and low latency of Wi-Fi 7 allow you to play online with minimal lag and no sudden disconnections. MLO technology ensures connectivity even when there are streamers in the house. With support for wide 320 MHz channels, 4K-QAM modulation, and Preamble Puncturing technology, game data is transmitted faster.
With the growing number of smart devices, your home network requires more bandwidth. Wi-Fi 7 easily handles cameras, sensors, voice assistants, thermostats, and other devices thanks to improved spectrum utilization and wider channels. Reduced latency ensures fast response times for lighting and security systems, while advanced modulation guarantees a stable connection. All this ensures smoother and more reliable operation of your smart home, even when you're watching 4K/8K video or using multiple apps at the same time.
Netcraze devices with Wi-Fi 7 support
In 2025, Netcraze released the Ultra (KN-1812) with Wi-Fi 7 support. The BE7200 class Wi-Fi 7 radio has a 4x4 MIMO configuration (4Tx4R:4SS) in the 2.4 GHz band and a 4x5 MIMO configuration (4Tx5R:4SS) in the 5 GHz band. The Wi-Fi 7 wireless network provides a maximum connection speed of up to 5764 Mbps (effective transfer of up to 4 Gbps) in the 5 GHz band for advanced 4x4 adapters or a Mesh system transport network, for example, with a similar model. With 2x2 adapters available in smartphones and laptops, this will be a link from 2882 (5 GHz) to 3570 Mbps in MLO mode (5+2.4 GHz).
Important
Actual performance and availability of Wi-Fi 7 features depend on the device. Before purchasing, please refer to the product specifications on our website for detailed information.